Even if you’re completely new to the world of crypto, surely by now you’ve heard of NFTs – you may have even heard the phrase “non-fungible tokens” – but what does that mean?
When an item is “fungible”, it means that it can be replaced and that it is divisible. Fungible tokens are cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ether and fiat currencies like the US dollar or the euro. So for example, you can exchange a 100 dollar bill for ten 10 dollar bills. The value is the same, it’s merely divided into smaller units. However, the reverse is the case for NFTs.
An NFT is “non-fungible”, meaning it cannot be replaced by something else, it’s unique. You can’t just exchange one NFT for another like you can with fungible tokens. Whether two NFTs are similar or different, you can’t trade one for the other. Non-fungible items are also impossible to divide. You cannot break down an NFT into smaller sections or “pieces”.
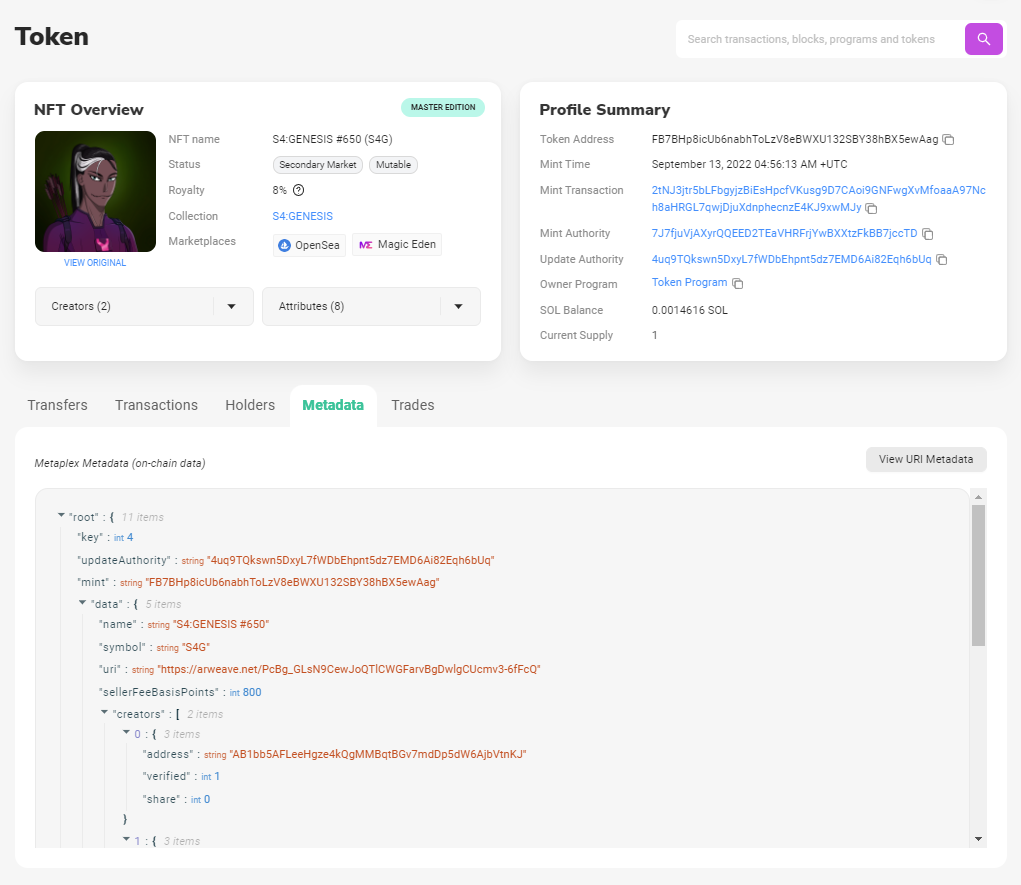
Essentially, an NFT is information (metadata) written on the blockchain about an asset (either digital or physical). NFTs are meant to represent assets so that by buying an NFT of a concert ticket you own the concert ticket itself. However, there are several reasons why this concept works a little differently in reality than it was first imagined.
Gfinity Esports revealed that the first ever NFT was created in 2014 by Kevin McCoy and Anil Dash. Fast-forwards a few years and we all know the story of Beeple selling his NFT art for over 69 million US dollars. From a short video clip that represented the first non-fungible token, the world of NFT has expanded to include various digital items. Examples of NFTs include digital art, tickets, collectibles, domain names, and many more!
NFT has also branched out to various audiences and different demographics. Hype Beast reported that the famous NBA player, Stephen Curry, launched his NFT collection in 2021. Businesses are also gradually adopting NFT by selling their products through this medium. Adopting NFT in the areas of businesses could improve credibility and authenticity.
In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the mechanics of NFTs in order to properly explain what they are. If you want to skip the more technical aspects, jump over to the section below explaining NFT art.
How does NFT work?
Let’s break down the more technical aspects of how NFTs work.
To start with: the technology behind NFTs is blockchain. All cryptocurrencies, as well as non-fungible tokens are built on the blockchain – a decentralized network responsible for verifying transactions. There are numerous networks in existence today, but one of the most popular is the Ethereum blockchain, which you may have heard of.
When we say that blockchain is decentralized, it means that it does not have a central authority, like a government. In traditional financial institutions like banks, there are people responsible for handling, verifying and storing transactions. However, in the case of blockchain, these actions are performed by every user on the network and the entire transaction history is public to everyone. And since everything is public, data manipulation is difficult.
One type of transactions written on the blockchain is transfer of ownership. When you buy an NFT, you are noted as the “buyer”, while the creator or previous owner of the NFT is noted as the “seller”. Blockchain makes it easy to track the life of a token, because all of the data is constantly recorded and cannot be deleted.
Since both cryptocurrencies and NFTs are stored on the blockchain, you need cryptocurrency to create, buy and sell non-fungible tokens. To better understand how all this correlates, imagine going to the arcade where you need a certain amount of “tokens” to play any of the games. You first exchange fiat currency (for example USD) for tokens and then you use them to play the arcade games. Similarly, you have to first exchange your fiat money for cryptocurrency and then buy NFTs on NFT marketplaces.
NFT art marketplace
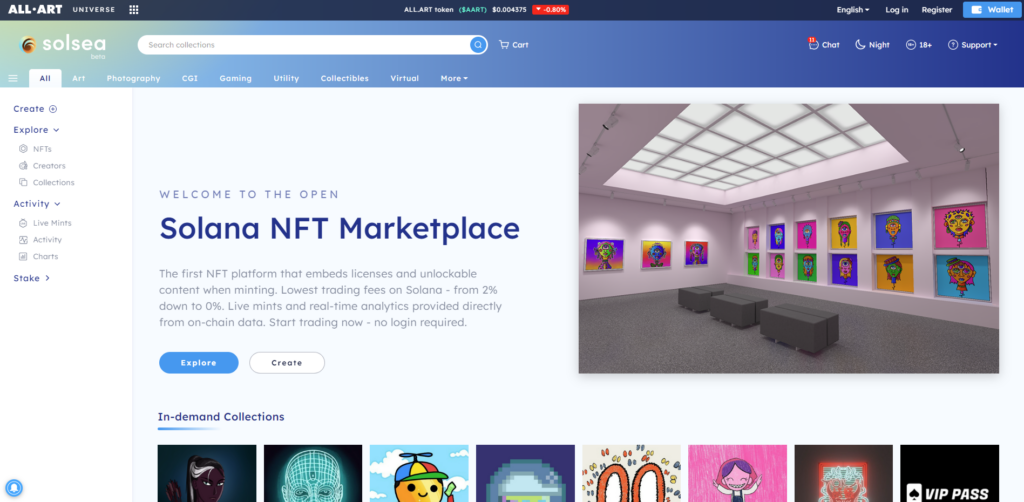
An NFT art marketplace is a platform where NFTs are displayed, bought, and sold. Think of it as an avenue for buyers and creators to trade. NFT marketplaces like SolSea and Rarible even allow creators to create NFTs on the platform before putting them up for sale. A big part of this process (called minting) is performed on the blockchain. The blockchain contains raw data that may not be comprehensive to the layman. This is why NFT marketplaces exist – to put minted NFTs on display.
An amazing thing about NFT marketplaces is that anyone can be a creator. Minting an NFT may seem a bit complex, but we got you covered! Check out our guide on how to create NFTs where we take you through the step-by-step process of setting up a crypto wallet, finding the right platform to create NFTs on, and how to promote and sell them.
As mentioned before, there are many different types of NFTs. They can represent anything from a digital image created by an artist or a 3D render of real estate to a website domain name or virtual sneakers your avatar can wear in the metaverse. Just like the activities of a conventional market, an NFT marketplace allows various types of NFTs to be sold.
We’ll take a closer look at NFT art to best illustrate what NFTs are and how they can be used.
What is NFT art?
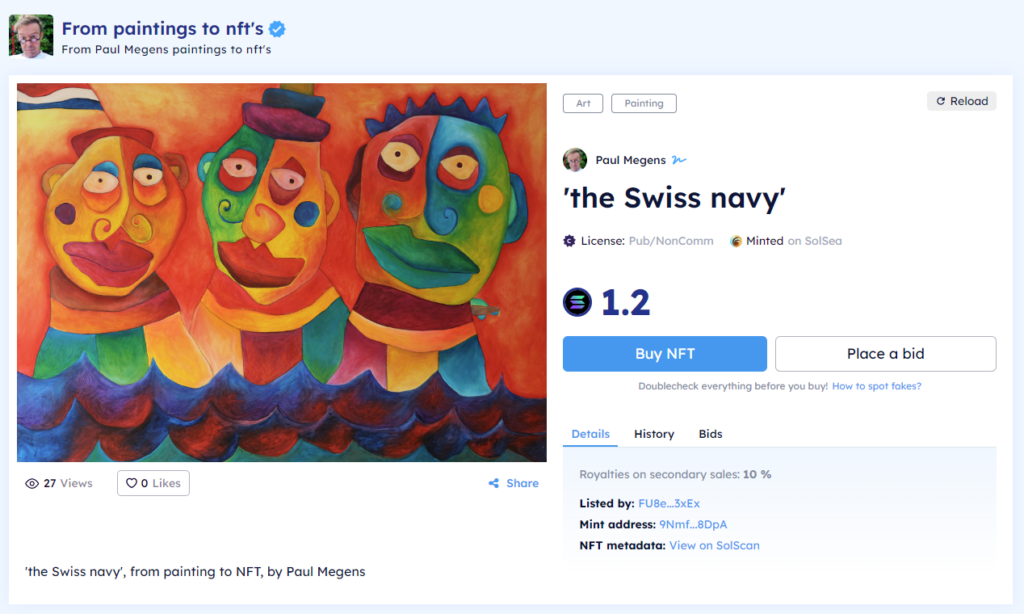
When a digital artist mints an NFT artwork, it means she uploaded her digital painting to a cloud storage service and wrote information about the image on the blockchain. This information is called “metadata” and paired with the link to her artwork stored on the cloud, it is an NFT. This non-fungible token then represents her digital painting, but it isn’t actually the painting itself. This is why in most cases, when you buy an NFT on a platform, you also get access to the image and the option to download it.
However, this comes with several issues with copyright as the artist may have never intended anyone else to have access to the original artwork because then what stops anyone with the file in their possession to redistribute or edit it. Buying an NFT doesn’t guarantee ownership of the asset the token represents.
This is why SolSea, an NFT art marketplace, introduced a unique feature in the NFT art space by allowing users to create NFTs with embedded copyright licenses. These licenses can help creators choose what future owners of their NFTs are legally allowed to do with their artworks.
How to earn with NFT?
Creators are not the only people that earn with NFT. Some people treat NFTs like proper investments.
Metaverse and gaming
The metaverse has been a hot topic in the digital world. It incorporates NFT, virtual reality, and augmented reality into a virtual world. In the metaverse, you can hold virtual meetings, attend virtual concerts, and watch various sceneries. But more interestingly, you can play and earn through gaming. When certain conquests are achieved, you may earn some tokens. Some NFT items like lands, and clothes, are also sold widely in the metaverse.
Create and sell an NFT
You can create your own NFT and showcase it to the world. Just like many other creators, you may profit from selling your NFT. Interested buyers may check out your NFT and make purchases. However, your NFT can gain more traction through promotions. To learn more, check out our guide on how to sell NFTs.
Royalties
Royalties are a percentage the original creator of an NFT receives from its secondary sales. When creating your NFT, you can set up a royalty percentage to generate passive income over time. However, if your royalties are too high, buyers may shy away from your NFT because it could cause them to gain less. As long as there’s frequent trading and your NFT keeps getting bought and resold, you’ll get royalties as its creator.
NFT flipping
NFT flipping is the process of buying an NFT and selling it at a higher price for profit. The demand for NFT helps flippers flourish and sell as many NFTs as they can. However, you should be careful because not every NFT project is a bang so there is still a possibility to make losses.
Hopefully this guide on NFTs taught you some interesting things about these tokens. Perhaps, you may consider getting into NFT as well! Remember that NFT has a place for everybody irrespective of interests. So whether you are a digital artist, an avid gamer, or an investor, you have a spot in the world of NFTs.
